Scientific Reproducibility Task Forces SOPThe contents of an approved ISEV Standard Operation Procedure (SOP) are provided below for ISEV member information. Authors: Rienk Nieuwland, Rossella Crescitelli, Le Thi Nguyet Minh, Ursula Sandau 1. Proposing a new task force: A new task force may be proposed by completing the official ISEV Scientific Reproducibility Subcommittee (SRS) survey, which is available on the ISEV task force webpage (https://www.isev.org/task-forces). Survey content The survey requests information on:
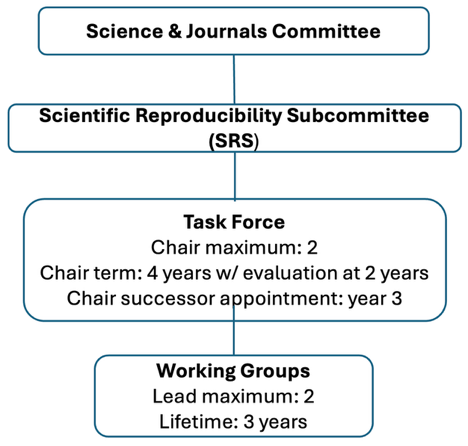
Eligibility to propose A potential chair may submit the survey themselves. Any ISEV member can propose a task force and include a suggested chair or co-chairs in the submission, provided those individuals have confirmed willingness to serve. All proposed chairs must be active ISEV members, established experts on the proposed EV topic, and be willing to dedicate time towards organizing the task force’s activities. Ideally, no more than two experts chair the task force. Review and approval process Proposal applications (https://www.isev.org/task-forces) are opened on an annual basis with a submission deadline in October. After which all proposals are reviewed at the first joint meeting of the SRS Chairs and the Science & Journals Committee. Following the discussion, applicants are notified of the outcome by email within approximately four to six weeks of the review meeting. Approved task forces are announced on the ISEV website, shared via ISEV communication channels, and formally introduced during the ISEV Annual Meeting. 2. Task force structure: Task forces are expert groups established under the ISEV SRS to strengthen the reproducibility of EV research. They contribute to the community by producing products such as position papers, guidelines, minimal reporting standards, databases (e.g., EV-TRACK), workshops, and other resources. Within each task force, smaller and temporary working groups may be created to deliver specific products or focus on dedicated objectives, advancing the overall progress of the task force. Any task force member may propose (and lead) a working group, and other task force members may join freely based on their interest and expertise. The lifetime of a working group is 3 years, in which a product or objective is expected to be delivered. Multiple working groups may operate simultaneously within a task force, and task force members are encouraged to contribute across more than one working group.
3. Responsibilities of task force chairs: The task force chairs, with input from task force members, define the overall objective of the task force, propose specific subobjectives and products, as well as support the working groups to deliver those in time. The task force chairs are also responsible for coordinating activities between the working groups, communication with the other task forces, and with the SRS. The term of the task force chair(s) is limited to 4 years in total, with an evaluation by task force members and SR chairs after 2 years. Evaluation will be based on an evaluation form, which summarizes the annual progress reports, completed activities, and members’ feedback. ISEV encourages task force chairs to identify and mentor their successor(s) at the beginning of year 3. Successors are ideally identified from among the task force working group leaders. The successor task force chair(s) should preferably, if possible, belong to a new and unrelated research group or laboratory, and also a different geographical chapter. Changes in task force chairs are meant to promote fresh ideas and outlooks, and to give in principle all task force members the opportunity to become a (co) leader of a task force. Nomination of new task force chairs must be approved by the SRS chairs. Responsibilities of task force chairs
4. Expectations of task force members: Each task force consists of ISEV members who are experts on the task force topic. Task force chairs must ensure that there is representation from different ISEV geographical chapters, different research groups/institutions, and gender balance. In addition, also representation from early career researchers is encouraged. Task force members can be recruited through membership surveys and virtual events (with support from ISEV’s management group), literature search, and professional networks. A task force can accept new members or remove inactive members during the task force lifetime at the discretion of the task force chairs. Inactive members are those who do not attend task force meetings, are generally not responsive, and do not help to achieve its goals. Involvement of ISEV members from the industry sector is supported by the ISEV board, and their involvement should be disclosed on the task force information webpage. Expectations of task force members
5. Managing a working group Each working group is co-led by 1 or 2 task force members. Working group leads are responsible for guiding the group's scientific direction, managing workflow, and ensuring the timely delivery of objectives. Key responsibilities of working group leads
Working group members are active contributors to the development and implementation of the task force’s initiatives. Members may come from diverse institutional, geographic, and career backgrounds, and are selected based on expertise and interest in advancing EV research relevant to the task force. Key responsibilities of working group members
6. Measuring progress and defining outputs To ensure transparency and accountability, task force chairs must track progress against pre-defined goals and timelines. Progress is measured both at the working group and task force levels. Annual progress reporting
The SRS chairs review reports, and provide constructive feedback and recommendations to ensure progress toward final outputs. Outputs Typical outputs include:
Quality assurance All outputs must undergo internal peer review by the task force and by the SRS co-chairs before submission. When appropriate, outputs will be disseminated through multiple channels (ISEV website, annual meeting, newsletters, webinars) to maximize reach and impact. 7. Discontinuation of a task force The discontinuation of a task force may occur upon successful completion of objectives, due to evolving scientific priorities or due to inactivity. The decision is formally made by the SRS chairs, with approval from the Science & Journals Committee. Discontinuation upon completion of outcomes
Discontinuation due to evolving scientific priorities
Discontinuation due to inactivity
Transition of ongoing work
Archiving and recognition
8. Communication with ISEV Members Surveys Membership surveys are a widely used tool to gather feedback from the EV community on challenges, needs, or specific topics identified by task forces.
Online events Task forces may wish to organize online events, such as webinars, member recruitment calls, or thematic workshops to recruit members, share preliminary results, gather feedback, or increase visibility of the task force:
ISEV Annual Meeting There will be a one to two hour SR session in the regular program dedicated to presenting ongoing task force activities, such as the introduction of new task forces and progress highlights. In addition, task forces are encouraged to organize satellite meetings that are independent from the main program of the annual meeting. These sessions can be used to meet task force members in person, review achievements, discuss next steps, and recruit new members. Furthermore, we strongly encourage joint sessions with other task forces, special interest groups or intersocietal working groups to foster collaboration and knowledge exchange. Proposals for satellite meetings are submitted in response to a survey circulated by the SRS approximately four months prior to ISEV annual meeting. All proposals are reviewed at the first joint meeting of the SRS co-chairs and the Science & Journals Committee. Following discussion, applicants are notified of the outcome by email within approximately four to six weeks of the review meeting. ISEV Website Task force webpages are the primary interface between the task force and the wider EV research community. Each task force webpage must include:
Updates should be submitted to ISEV’s Management Group via [email protected] Document repository ISEV will maintain a secure online repository (SR folder) where all documents related to task forces (e.g., meeting minutes, drafts, survey data) are stored. Access is provided to task force chairs, SRS co-chairs and Science and Journals committee to ensure continuity and transparency. 9. Support of task forces by SRS Key responsibilities of SRS co-chairs
10. Support by ISEV scientific reproducibility grants ISEV aims to improve reproducibility of EV research by funding projects aimed to promote scientific reproducibility efforts of ISEV task forces, special interest groups and inter-societal working groups. Collaborative projects between task forces, special interest groups, or inter-societal working groups are encouraged and may be also considered for the grant support. ISEV aims to support as many competitive projects as possible, within the yearly ISEV budget. ISEV SR grants may be allocated to pay for direct costs (e.g. shipping and related consumable costs for inter-laboratory studies), but do not cover salaries, indirect costs or travel costs. Applicants must be a) ISEV members, and b) active members of a task force, special interest group or an inter-societal working group. Applications can be submitted through the SurveyMonkey link at the ISEV task force webpage (https://www.isev.org/task-forces) which is opened for applications on an annual basis with a submission deadline in November. Project proposals will be reviewed by the ISEV SR grant committee, consisting of the ISEV SRS co-chairs, one Science & Journals committee member, and two independent EV experts. Following discussion, applicants are notified of the outcome by email within approximately four to six weeks. Awardees will be announced during the General Assembly at the annual ISEV meeting. ISEV expects that the funding is acknowledged in scientific outreach as publications, web sites and presentations, and that results will be presented within two years at the annual ISEV meeting. 11. Belonging, respect, and fairness The ISEV leadership, SRS and associated task forces are committed to fostering an inclusive, respectful, and scientifically diverse environment that promotes collaboration across disciplines, regions, and identities. While the primary mission of a task force is technical and scientific in nature, we recognize that the strength of our work relies on broad participation from researchers of diverse backgrounds and perspectives. Objectives
Implementation practices
12. Professional communication standards As a collaborative, multidisciplinary effort, the ISEV task forces value professionalism, transparency, and clear communication. All members are expected to engage constructively and represent the task force and its mission with integrity. Communication principles
Back to Scientific Reproducibility |